The following is an internal memo that I shared with Coinbase employees this week and would also like to share publicly to help people see how we’re working toward our mission of increasing economic freedom in the world.
Tl;dr: Our core thesis is that greater adoption and usage of cryptocurrency will increase economic freedom in the world, because crypto solves many of the shortcomings of the current financial system that hinder economic freedom.
Team,
Every quarter at our company All Hands, we review our Mission (what we’re trying to achieve) and our Strategy (how we’re going to get there). One question I often hear from employees is: “How does cryptocurrency create more economic freedom in the world?” This is a great question, so I wanted to share my thoughts with all of you.
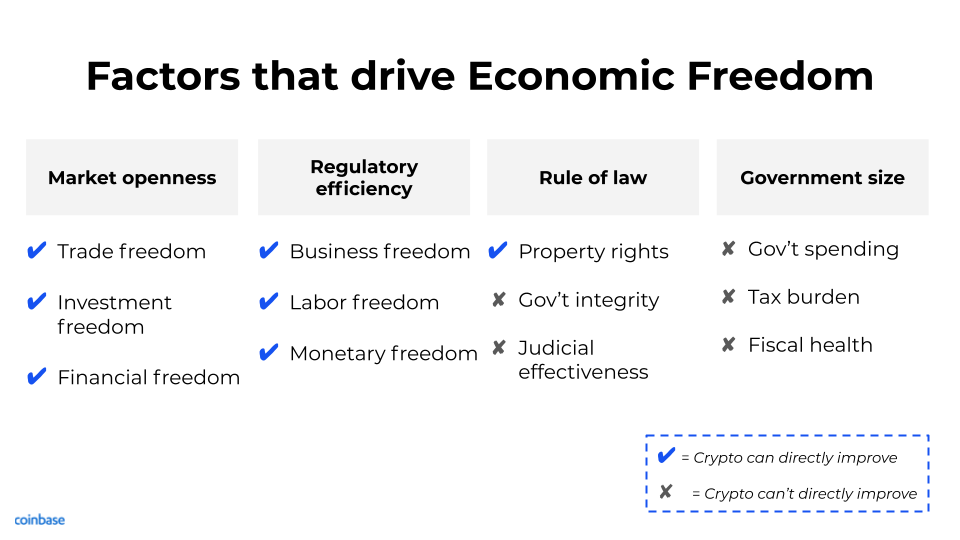
First, a refresher: Economic freedom is a composite measure of 12 factors. It quantifies the rights of people to control their own labor and property in each country and globally. Economic freedom varies dramatically across the world, and while our economy is increasingly global, the government of any single country has significant control over the financial and economic freedoms of its people. Low economic freedom in a given country isn’t always due to malicious activity (e.g, fraud, oppression, etc) — it’s often due to mismanagement (poor monetary and fiscal policy) or simply bad infrastructure.
Crypto and economic freedom
The question to ask is: How can we build a global economy where anyone with an internet connection can participate, where property rights are enforced, and where money preserves its value? Crypto is the solution. Crypto can’t directly improve every facet of economic freedom (e.g., tax policies and government spending), but it can improve most of the underlying drivers (see below).
Why is crypto so uniquely positioned to increase economic freedom? Because it has these inherent properties:
Crypto is an open, global network
Crypto networks are open, removing the barriers of borders. It allows every person in the world to transact on shared networks, in the same way they communicate on a shared network (the internet). More importantly these networks themselves are not controlled by governments that can use their monetary systems to hinder economic freedom (and prosperity). This design principle leads to more open markets and increases trade freedom, investment freedom, financial freedom, and monetary freedom.
Crypto enforces property rights
Property rights allow people to save their income, grow their wealth, and plan for the long term because they know the fruits of their labor are safe from unfair seizure or theft. Before crypto, your confidence in property rights was a function of the trust you had in your government and its respect for the rule of law. With crypto, anyone can acquire and grow their wealth without intervention from trusted 3rd parties like a government or a bank, or fear that their wealth could easily be seized. Property rights are also about the ability to enter contractual agreements. In some areas around the world, a contract has little value, because you can’t be confident in its enforcement. Smart contracts move enforcement from the courts to the blockchain, enabling gains from specialization and commercial exchange.
Crypto is unbiased
Crypto networks are often pseudonymous (or even anonymous). They don’t care where you live, what your race or gender is, or who you voted for in the last election. Unlike the current financial system they are inherently open and unbiased. Anyone with an internet connection can create a wallet, get paid in crypto, spend in crypto and accrue wealth in crypto. Service providers like Coinbase do have compliance programs as required by law, but we don’t control access to all crypto and we don’t own the network. Anyone can access crypto networks through other providers if we make a bad decision, or are forced into bad regulation. In addition, self custody wallets like Coinbase Wallet provide an ever greater degree of freedom when it comes to financial inclusion.
Crypto enables mobility
As I mentioned above, there are important components of economic freedom that cryptocurrency can’t directly benefit (e.g., government integrity, tax policies, fiscal health, etc.). However, cryptocurrency does provide the conditions for mobility by reducing switching costs, allowing people to both accrue wealth and bring it across borders. Cryptocurrency is the ultimate embodiment of the power of the individual, by significantly reducing the barriers to emigration / exit, and thus increasing economic freedom.
Conclusion
As you can see, cryptocurrency can impact many of the factors that lead to more economic freedom. It can both help build better-functioning economies in countries with less economic freedom, and make it easier to emigrate to a better life. This is why our core thesis as a company is that greater adoption and usage of cryptocurrency will increase economic freedom in the world.
Technology is the longest lever we can pull to improve the human condition. At its core, cryptocurrency is a technology breakthrough that allows us to build a more free and open financial system that enables the rights of people to control their own labor and property. It is the best tool that exists to advance our mission of increasing economic freedom in the world.
What does this mean for Coinbase? Crypto is in many ways still nascent. It’s still hard to use, crypto networks are plagued with scaling challenges, and the economy built on top of crypto infrastructure is in its early days. Our strategy and roadmap is geared towards solving these challenges: We’re focused on building easy-to-use products that abstract away the complexity of blockchains, and we’re building the primitives of a functioning financial system. We still have a long way to go, but the future is bright.
How crypto enables economic freedom was originally published in The Coinbase Blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.